Crop Physiology
Roles of Root Aerenchyma Development and Its Associated QTL in Dry Matter Production under Transient Moisture Stress in Rice
J.M. Niones, R.R. Suralta, Y. Inukai and A. Yamauchi
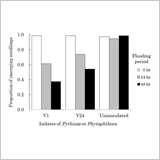
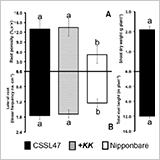
- The quantitative trait loci (QTLs) associated with the plasticity in aerenchyma development under transient drought-to-waterlogged (TD-W) stress were analyzed with a mapping population of 60 F2 genotypes of chromosome segment substituted lines (CSSL) derived from CSSL47 and Nipponbare crosses grown in rootboxes
- At LOD > 2.5, the QTL associated with aerenchyma development was mapped on the short-arm of chromosome 12 regions and designated as qAER-12.
- The effect of qAER-12 on the plasticity in aerenchyma development under TD-W was significantly associated with the increase in lateral root elongation and branching, resulting in greater root system development and higher dry matter production.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1601K] |
 |
Responses of Eighteen Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars to Temperature Tested using Two Types of Growth Chambers
E.M. Pasuquin, T. Hasegawa, P. Eberbach, R. Reinke, L.J. Wade and T. Lafarge
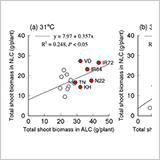
- Artificially- and naturally-lit chambers (ALC & NLC) were used to test temperature responses of 18 cultivars.
- The optimum temperatures differed between ALC and NLC, but cultivar performance was similar.
- IR64, IR72, N22, Vandana, Takanari and Koshihikari showed higher adaptability to high temperatures.
Abstract Full Text PDF[708K] |
 |
Maturation Changes in Seed Quality of Sunflower under High or Changeable Water Table Conditions.
S. Yasumoto and M. Matsuzaki
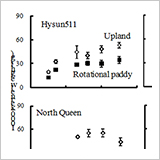
- The growth and the seed and oil yields of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) were significantly lower in a rotational paddy field than in an upland field.
- In a maturing period, oil accumulated in seeds until about 25 days after flowering in both fields, but less in the rotational paddy field than in the upland field.
- Although the temporal patterns of fatty acid compositions during seed maturation were similar in both fields, the oleic acid content tended to be lower in the rotational paddy field even under the same climatic conditions and ripening periods.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1301K] |
 |
Genetic Resources Evaluation
Genotypic Variation in Nitrogen Uptake during Early Growth among Rice Cultivars under Different Soil Moisture Regimes
M. Matsunami, T. Matsunami, K. Kon, A. Ogawa, I. Kodama and M. Kokubun
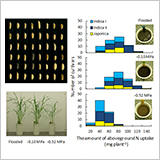
- Genotypic variation among diverse rice cultivars in N uptake and N use efficiency under different soil moisture regimes was examined.
- A substantial genotypic variation in N uptake ability existed under water deficient conditions.
- N uptake ability was correlated with water uptake ability, while genotypic variation in N uptake per unit water uptake was found in non-flooded regimes.
Abstract Full Text PDF[2111K] |
 |
Accurate Evaluation of Photoperiodic Sensitivity and Genetic Diversity in Common Buckwheat under a Controlled Environment
T. Hara and R. Ohsawa
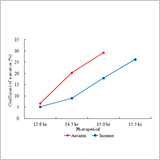
- The summer ecotype consisted of early-flowering genotypes. On the other hand, the autumn ecotype consisted of early-flowering and late-flowering genotypes.
- The autumn ecotype showed larger genetic diversity than the summer ecotype in long-day treatments.
- These results support the hypothesis based on previous studies that summer ecotypes were derived from autumn ecotypes.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1026K] |
 |
Agronomy & Crop Ecology
Does Allelopathy Play a Role in Suppression of Mugwort (Artemisia vulgaris) by Alfalfa?
H. Onen
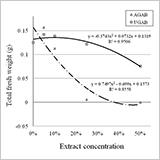
- Soil incorporated not ‘Under-Ground’ but ‘Above-Ground’ Alfalfa Biomasses was highly inhibitory on sprouting of mugwort rhizome fragments and growth of seedlings in a dose-dependent manner.
- Although the growth of mugwort seedlings was not significantly affected by post-emergence applied alfalfa extracts, the seed germination and seedling growth were significantly reduced with the water extracts of both ‘Under-Ground’ and ‘Above-Ground’ Alfalfa Biomasses in petri dish experiments.
- The allelopathic effect of alfalfa along with competitive ability and harvesting regime may play important role in suppressing mugwort growth.
Abstract Full Text PDF[713K] |
 |
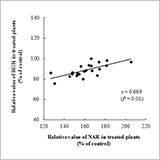
Comparison of Young Seedling Growth and Sodium Distribution among Sorghum Plants under Salt Stress
J. Chaugool, H. Naito, S. Kasuga and H. Ehara
- The decrease in plant dry weight of Sorghum under NaCl stress was attributed to relative growth rate (RGR) associated with the change in net assimilation rate (NAR).
- Sorghum plants retained Na+ mainly in the roots preventing the Na+ distribution to the leaf blades.
- The thicker leaf blades and an increase in root dry weight enhanced the growth of Sorghum cultivars under salt treatment.
Abstract Full Text PDF[946K] |
 |
Improvement of Rice Seedling Establishment in Sulfate-applied Submerged Soil by Seed Coating with Poorly Soluble Molybdenum Compounds
Y. Hara
- Effect of seed coating on rice seedling establishment in sulfate-applied soil was investigated.
- Seed coating with poorly soluble molybdenum compounds improved the rice seedling establishment.
- Ammonium phosphomolybdate, potassium phosphomolybdate and molybdenum trioxide were more effective.
Abstract Full Text PDF[631K] |
 |
Grain Yield and Leaf Area Growth of Direct-seeded Rice on Flooded and Aerobic Soils in Japan
M. Okami, Y. Kato and J. Yamagishi
- Yield stability of direct-seeded rice was lowered by the water-saving irrigation, compared to flooded conditions.
- Poor performance of direct-seeded rice under aerobic conditions was associated with reduced leaf growth during the vegetative stage.
Abstract Full Text PDF[543K] |
 |
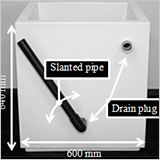
Alternative Experimental Method Using a FRP Pot for Evaluating Wet Damage in Soybean and Morning Glory Grown under Excess Soil Water Condition
S. Asakura, C. Noma, A. Matsumura and H. Daimon
- A FRP pot was used for evaluation of wet damage of soybean and morning glory.
- Percentage of ureide-N in xylem sap of soybean was 81% under excess soil water condition.
- Pitted morning glory might be more wet tolerant than entire leaf morning glory.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1519K] |
 |