Crop Morphology
Root Anatomical Traits and Their Possible Contribution to Drought Tolerance in Grain Legumes
Ramamoorthy Purushothaman, Mainassara Zaman-Allah, Nalini Mallikarjuna, Rajaram Pannirselvam, Lakshmanan Krishnamurthy and Cholenahalli Lakkegowda Laxmipathi Gowda
- Xylem vessel size and the number were the most discriminating drought-response traits.
- Pigeonpea used water conservatively as it had a few narrow xylem vessels.
- Chickpea and cowpea had moderate xylem passage with moderate water absorption and were equipped for drought episodes.
- The greater adaptation of common bean, soybean and cowpea to rainy season was likely due to the presence of moderate number of large vessels.
- Soybean and pigeonpea had a relatively thinner cortex offering less resistance to water conductance.
- The proportional development of cortex and stele was also influenced by soil moisture environment.
Abstract Full Text PDF[3282K] |
 |
A Quick Method to Estimate Root Length in Each Diameter Class Using Freeware ImageJ
Ryosuke Tajima and Yoichiro Kato
- Root lengths assigned to root diameter classes estimated with our proposed method were compared with those estimated with WinRHIZO.
- We proposed completely automated estimation of root lengths.
Abstract Full Text PDF[656K] |
 |
Crop Physiology
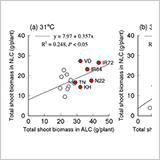
Role of Canopy Coverage in Water Use Efficiency of Lowland Rice in Early Growth Period in Semi-Arid Region
Tetsuji Suzuki, Takeshi Ohta, Yasuhiro Izumi, Luke Kanyomeka, Osmund Mwandemele, Jun-Ichi Sakagami, Koji Yamane and Morio Iijima
- WUE of lowland rice was significantly correlated with the number of tillers, and higher planting density resulted in a higher WUE.
- To increase WUE in semi-arid regions, the increase of canopy coverage and higher planting density are recommended.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1071K] |
 |
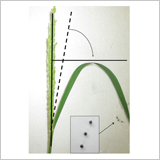
Inclination Angle Affects Ozone Injury in the Flag Leaf of Rice
Hiroki Kobayakawa and Katsu Imai
- The effect of rice leaf inclination angle on the leaf injury by O3 was evaluated.
- The weaker inhibitory effect of O3 on the erect leaf depended on the lower light intensity at the leaf surface, rather than the horizontal leaf position.
Abstract Full Text PDF[833K] |
 |
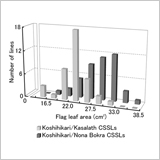
Identification of Chromosome Regions Affecting Leaf Area with Rice Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines
Kazuhiro Ujiie and Ken Ishimaru
- With Nona Bokra allele, the region on chromosome 7 (LA7) increased leaf area by 54%.
- LA7 maintained the Rubisco content and photosynthetic rate at the same level as Koshihikari.
- As a result, its “estimated” source ability of a flag leaf was increased by 23%.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1108K] |
 |
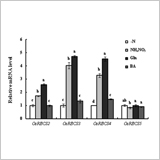
Effects of Nitrogen on the Expression of Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase Small Subunit Multigene Family Members in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
Nobuo Miyazaki, Osamu Ueno and Kazuyuki Saitou
- The expression of five ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase small subunit genes (OsRBCS) identified in the rice (Oryza sativa) genome was analyzed
- The mRNA levels of OsRBCS2, OsRBCS3, and OsRBCS4 in leaf blades were increased by NH4NO3 or glutamine supply to detached shoots.
Abstract Full Text PDF[738K] |
 |
Genetic Resources Evaluation
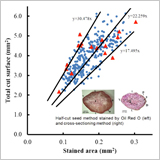
Close Association between Aleurone Traits and Lipid Contents of Rice Grains Observed in Widely Different Genetic Resources of Oryza sativa
Ohn Mar Khin, Masao Sato, Tong Li-Tao, Yuji Matsue, Atsushi Yoshimura and Toshihiro Mochizuki
- We found wide variation in aleurone traits among rice varieties.
- There was a strong correlation between the area of the aleurone layer and the stained area by Oil Red O.
- The amount and proportion of triacylglycerol of brown rice were both significantly correlated with the aleurone traits.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1118K] |
 |
Agronomy & Crop Ecology
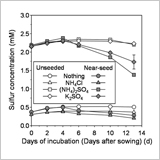
Suppressive Effect of Sulfate on Establishment of Rice Seedlings in Submerged Soil May be Due to Sulfide Generation around the Seeds
Yoshitaka Hara
- Redox potential near seeds dropped rapidly to levels that allowed harmful sulfide ion generation.
- Sulfur concentration in the soil solution decreased, thereby also implying sulfide ion generation.
- Sulfate ions would change into sulfide ions near seeds, impairing the seedling establishment.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1113K] |
 |
Improvement of Rice Seedling Establishment in Sulfate-Applied Submerged Soil by Application of Molybdate
Yoshitaka Hara
- The application of molybdate improved the rice seedling establishment in sulfate-applied soil.
- The application of molybdate delayed the decline of the sulfur concentration in the soil solution.
- Molybdate would suppress the generation of sulfide ions, which are harmful to establishments.
Abstract Full Text PDF[971K] |
 |
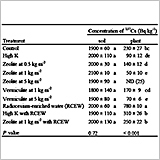
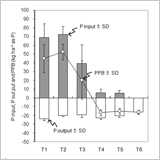
Phosphorus Balance and Soil Phosphorus Status in Paddy Rice Fields with Various Fertilizer Practices
Toshiyuki Nagumo, Shintaro Tajima, Sanae Chikushi and Ayako Yamashita
- In paddy soils having excessive accumulation of soil P, rice P uptake was approximated to be 20 kg ha−1, irrespective of the P input ranged from 0 to 73 kg ha−1 yr−1.
- Slight differences in rice P uptake among plots was implied that rice P uptake was determined by nitrogen fertilization rather than P input as well as soil P status.
- Additional P input increased the soil P wastefully, and only enhanced the risk of P runoff.
- Therefore, P fertilization should be restricted to 20 kg
ha-1 yr-1 (corresponding to 46 kg ha-1 yr-1 as P2O5), at most.
Abstract Full Text PDF[932K] |
 |
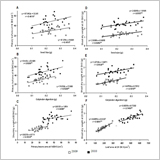
Varietal Difference in Early Vegetative Growth during Seedling Stage in Soybean
Fatichin, Shao-Hui Zheng and Susumu Arima
- The varietal difference in the growth parameters during the seedling stage was investigated in soybean.
- Big seeds with rapid cotyledon digestion developed a wider leaf area and therefore large dry matter production.
- The conversion of stored energy was more important than the leaf photosynthetic activity for early growth.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1031K] |
 |
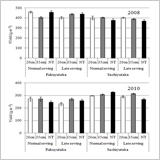
Growth and Yield Responses of Two Soybean Cultivars Grown under Controlled Groundwater Level in Southwestern Japan
Naoki Matsuo, Motoki Takahashi, Hiroshi Nakano, Koichiro Fukami, Shinori Tsuchiya, Satoshi Morita, Hisashi Kitagawa, Keiko Nakano, Hiroaki Nakamoto and Kohei Tasaka
- The yield of Sachiyutaka tended to be increased by groundwater level control by FOEAS, especially in late sowing treatment.
- On the other hand, if Fukuyutaka was late-sown, the yield of Fukuyutaka was decreased by groundwater level of 20cm.
- These results indicated that the effect of groundwater level control on yield differed among cultivars.
Abstract Full Text PDF[959K] |
 |
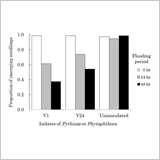
Association of Pythium and Phytophthora with Pre-emergence Seedling Damping-off of Soybean Grown in a Field Converted from a Paddy Field in Japan
Masayasu Kato, Keisuke Minamida, Motoaki Tojo, Takuo Kokuryu, Hideo Hamaguchi and Shinji Shimada
- Pre-emergence soybean seedlings survived 48-hr flooding in the absence of oomycete microorganisms.
- The oomycetes caused more seedling damage as the flooding period increased.
- The seedling damage was reduced with the treatment of mancozeb+metalaxyl.
Abstract Full Text PDF[2149K] |
 |