Crop Physiology
Cleistogamy decreases the effect of high temperature stress at flowering in rice
S. Koike, T. Yamaguchi, S. Ohmori, T. Hayashi, O. Yatou and H. Yoshida
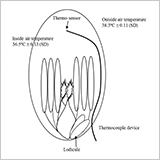
- The aim of this study was to determine the role of cleistogamy (closed flowering) in avoiding high temperature-induced sterility.
- The cleistogamous rice plants showed a higher fertility percentage and a larger number of germinated pollen grains on a stigma than the chasmogamous rice plants at 38°C for 4 h at flowering.
- The temperature inside the closed flowering spikelets was 1.8°C lower than that outside the spikelets.
Abstract Full Text PDF[891K] |
 |
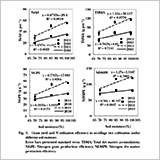
Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization by No-Tillage Rice under Different Soil Moisture Conditions – A Model Study under Simulated Soil Conditions
C. Yang, S. Xu, L. Liu, M. Huang, T. Zheng, S. Wei, Y. Zhang, G. Deng and L. Jiang
- N uptake and yield were decreased by decreasing soil moisture contents to 70% of saturation in no-tillage cultivation.
- Soil moisture mainly affected fertilizer N uptake, but hardly affected soil indigenous N uptake.
- Soil content of around 85% was proposed as a suitable condition without a large reduction in the yield and N use.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1202K] |
 |
QTLs for Shoot Length and Chlorophyll Content of Rice Seedlings Grown under Low-Temperature Conditions, using a Cross between Indica and Japonica Cultivars
A. Fukuda and T. Terao
- QTLs for the shoot and culm length were detected on the same region of chromosome 1 including SD1.
- Other QTLs for the shoot length but had no effect on the culm were detected on chromosomes 3 and 8.
- A novel QTL for the chlorophyll content was detected on chromosome 1.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1078K] |
 |
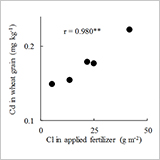
Effects of Ammonium Chloride Fertilizer and its Application Stage on Cadmium Concentrations in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Grain
N. Ishikawa, G. Ishioka, M. Yanaka, K. Takata and M. Murakami
- Cd concentration of wheat grain was higher with NH4Cl fertilizer than with (NH4)2SO4 or urea.
- Grain Cd in wheat topdressed with NH4Cl was 0.22 mg kg-1, 1.5 times higher than that with urea.
- We recommend the use of (NH4)2SO4 or urea in place of NH4Cl as the nitrogen fertilizer.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1065K] |
 |
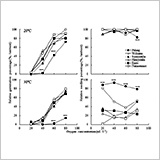
Does Pre-Germination Flooding-Tolerant Soybean Cultivar Germinate Better under Hypoxia Conditions?
T. Nakajima, A. Seino, T. Nakamura, Y. Goto and M. Kokubun
- Seeds of all 6 cultivars hardly germinated under an oxygen concentration of 20 mL L-1, but germinated with increasing oxygen concentration regardless of temperature.
- Seven days after termination of 3-d hypoxia treatment at 30°C, the percentage of seedlings with root hairs and/or lateral roots relative to that after ambient oxygen treatment was maintained in ‘Peking’ but decreased in the other cultivars, especially in ‘Nakasennari’.
- Pre-germination flooding-tolerant cultivar, especially ‘Peking’, is characterized by a delay in germination processes under hypoxia, and exhibits vigorous germination after release from hypoxia.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1472K] |
 |
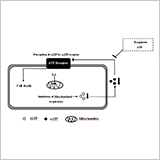
Extracellular ATP is Involved in the Salicylic Acid-Induced Cell
Death in Suspension-Cultured Tobacco Cells
H. Feng, D. Guan, K. Sun, Y. Fang, Y. Zhao
and L. Jia
- SA-induced cell death was campaigned by decreases of eATP, iATP and respiratory rate.
- AMP-PCP, an inhibtor of eATP receptor, also induced cell death.
- Exogenous ATP partially alleviated the cell death induced by SA.
Abstract Full Text PDF[897K] |
 |
Improvement of Soybean Seedling Establishment under a Flooded
Condition by Seed Coating with Molybdenum Compounds
Y. Hara
- Effect of seed coating on soybean seedling establishment after flood condition was investigated.
- Seed coating with molybdenum compounds improved seedling establishments after flood condition.
- In soybean, seed coating with molybdenum compounds could improve the flooding damage after sowing.
Abstract Full Text PDF[745K] |
 |
Genetic Resources Evaluation
Stability Verification of the Effects of Stem Determination and
Earliness of Flowering on Green Stem Disorder of Soybean against
Genetic Background and Environment
K. Fujii, S. Kato, T. Sayama, Y. Tanaka, T. Nakazaki,
M. Ishimoto and T. Shiraiwa
- We investigated the effects of developmental traits on the severity of green stem disorder (GSD) in soybean.
- The genetic factor influencing the severity of GSD was detected around the stem determination locus (Dt1), but it was uncertain whether the responsible gene was the stem determination gene itself.
- The genetic factor around the Dt1 locus seemed to interact with earliness of flowering in relation to the severity of GSD.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1492K] |
 |
Agronomy & Crop Ecology
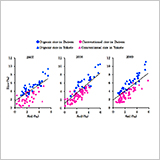
Characteristics of the Relationship between Natural 15N Abundances
in Organic Rice and Soil
M. Nishida and Y. Sato
- We examined δ15N values of rice and soil in organic farming and conventional farming.
- Regression line was obtained between δ15N values of rice and soil without N source application.
- That regression line can aid in discriminating organic rice from conventional rice.
Abstract Full Text PDF[851K] |
 |
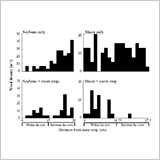
Interseeding a Cover Crop as a Weed Management Tool is More
Compatible with Soybean than with Maize in Organic Farming
Systems
H. Uchino, K. Iwama, Y. Jitsuyama, T. Yudate,
S. Nakamura and J. Gopal
- Weed density was higher in maize than in soybean within the row, but it was higher in soybean between the rows.
- The difference in ground cover was one of the reasons causing the difference in weed density between the two main crops.
- Cover crops could not decrease sufficiently the high weed density within the row of maize.
Abstract Full Text PDF[894K] |
 |
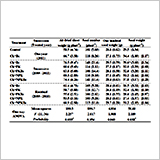
Continuous Application of Biochar Inoculated with Root Nodule
Bacteria to Subsoil Enhances Yield of Soybean by the Nodulation
Control using Crack Fertilization Technique
M. Iijima, K. Yamane, Y. Izumi, H. Daimon
and T. Motonaga
- Soybean seed weight significantly increased by the application of nodule bacteria on biochar for three successive years.
- Nitrogen fixation activities significantly increased in the soybean plants grown on the soil collected from the subsoil to which the biochar had been applied.
- Thus, the crack fertilization technique leads to yield enhancement when nodule bacteria on biochar are continuously applied.
Abstract Full Text PDF[1047K] |
 |
Growth Behavior of Sago Palm (Metroxylon sagu Rottb.) from
Transplantation to Trunk Formation
K. Nabeya, S. Nakamura, T. Nakamura, A. Fujii,
M. Watanabe, T. Nakajima, Y. Nitta and Y. Goto
- In sago palm, the horizontal stem elongation stops at around 6.5 years after transplantation of sucker and the stem growth curve shows a sigmoidal curve.
- The stem growth stage of a transplanted sucker is divisible into three stages based on its elongation direction: the creeping growth stage, the trunk formation stage, and the trunk elongation stage.
- The creeping growth stage is an important period because the standing positions of trunks are determined.
Abstract Full Text PDF[5131K] |
 |
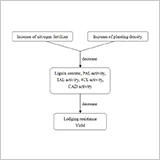
Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Planting Density on the Lignin
Synthesis in the Culm in Relation to Lodging Resistance of
Buckwheat
C. Wang, R.W. Ruan, X.H. Yuan, D. Hu, H. Yang,
Y. Li and Z.L. Yi
- The Lignin synthesis is closely related to the lodging resistance of culm in buckwheat.
- Increasing nitrogen fertilizer will decrease the lignin content and its related enzymes activities.
- Increasing planting density will decrease the lignin content and its related enzymes activities.
- Increasing nitrogen fertilizer and planting density will increase the risk of culm in buckwheat.
Abstract Full Text PDF[626K] |
 |
Response of 10 Elite “Green Super Rice” Genotypes to Weed
Infestation in Aerobic Rice Systems
B.S. Chauhan, J. Opeña and J. Ali
- 10 GSR genotypes were studied at partial (PWC) and moderate weed control (MWC) in dry-seeded rice.
- In PWC plots, the IR83140-B11-B performed well, resulting in 2850 and 4610 kg ha-1 in two seasons.
- The yield loss of this genotype in PWC relative to MWC was only 10-21% in different seasons.
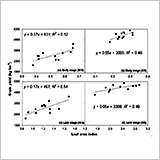
- Results showed positive correlation between grain yield and leaf area at early stage of the crop.
- Genotypes with greater leaf area need to be integrated with other weed control methods in rice.
Abstract Full Text PDF[690K] |
 |
Short Report
Early-Maturing and Chilling-Tolerant Soybean Lines Derived from
Crosses between Japanese and Polish Cultivars
N. Yamaguchi, H. Kurosaki, M. Ishimoto,
M. Kawasaki, M. Senda and T. Miyoshi
- Two breeding lines derived from crosses between Japanese and Polish cultivars, Tokei 1067 (T1067) and Toiku 251 (T251), had a significantly earlier maturing time than Yukihomare (YH).
- The seed yield of T251 was similar to that of YH.
- The chilling tolerance levels of the T1067 and T251 lines at the flowering stage were greater than the tolerance level of YH.
Abstract Full Text PDF[778K] |
 |